“Pollution flashover” refers to the deposition of dust particles in the atmosphere on the surface of insulators that have been operating outdoors for a long time, gradually forming a pollution layer. Under meteorological conditions such as light rain, snow, fog, haze, and dew, the pollution layer gradually becomes moist, and the soluble substances in it gradually dissolve in water, forming a conductive film on the surface of the insulator, thereby increasing the surface conductivity, reducing the insulation performance, and causing flashover discharge on the wet surface of the insulator.

The insulator is an electrical component whose main function is to isolate the electrical connector between the conductor and the supporting structure to prevent the current from flowing through the supporting structure or causing an arc fault. The reasonable selection and use of insulators is crucial to ensure the safe and stable operation of the power system. Among them, composite insulators have high cost performance due to their strong pollution resistance, high strength, lightness, and non-fragile properties, which are in line with the trend of green development. Among them, the insulating parts of the composite insulator are composed of a epoxy resin fiber glass core rod, a silicone rubber sheath shed (which plays a key insulating and anti-fouling performance).
Composite insulators are equivalent to putting on “protective clothing” for transmission line equipment, reducing the impact of different harsh environments or corrosive environments on the electrical and mechanical properties of the transmission system, further reducing the failure rate of the power system, reducing the possibility of pollution flash accidents, saving operation and maintenance costs, and improving the utilization rate of electric energy.
So how does fumed silica work?
Fumed silica mainly plays a thickening and thixotropic role in composite insulators and anti-pollution flashover coatings, which can improve the physical and mechanical properties, hydrophobicity, and electrical properties of anti-pollution flashover coatings. In order to verify the specific improvement effect of fumed silica on composite insulators, the technicians prepared two groups of samples, namely blank samples (fumed silica), experimental samples (adding hydrophobic fumed silica), and then tested their differences in elongation at break, tensile strength, flame retardancy, dielectric strength and hydrophobicity, and obtained the data results in Table 1.
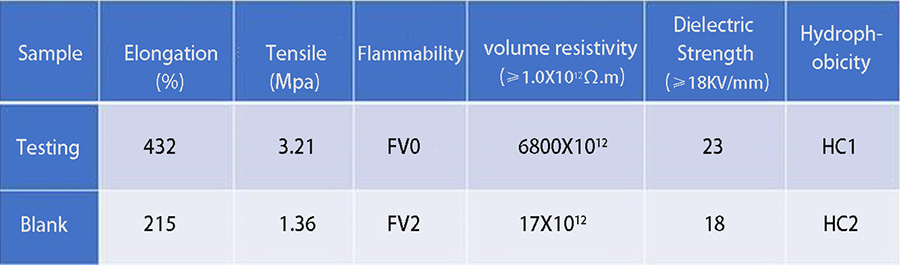
Table 1
After experimental comparison, fumed silica can effectively improve the physical properties of composite insulators, enhance flame retardancy and hydrophobicity, and improve volume resistivity and dielectric strength.
After adding fumed silica, the composite insulator provides multiple functions such as electrical insulation, mechanical support, and environmental adaptability with its excellent hydrophobicity, pollution flashover resistance, high electrical insulation, and strong corrosion resistance, ensuring the safe, stable, and reliable operation of transmission lines and further promoting the development of clean energy.