Normally the voltage class of power line can be divided into 10 kV, 35 kV, 110 kV, 220 kV, 500 kV ultra-high voltage, ±800 kV UHV.
In our life, we will also see various heights different shapes of transmission lines and towers, so, how do us to distinguish voltage class?
Towers generally erect high-voltage lines, which are 35 kV and above; single poles mainly erect medium and low-voltage lines, generally 10 kV and below.
DC has only positive and negative poles; AC has three phases, with three or six wires (six wires on the same tower are double-circuit lines on the same tower).
What is the number of wire splits? As the name suggests, split wire is to fix several wire bundles together to replace the original wire to suppress corona discharge, optimize line parameters, and improve the transmission capacity of the line and the stability of the power system operation.
The splitting situation of AC transmission lines is as follows:
Single-split conductors:
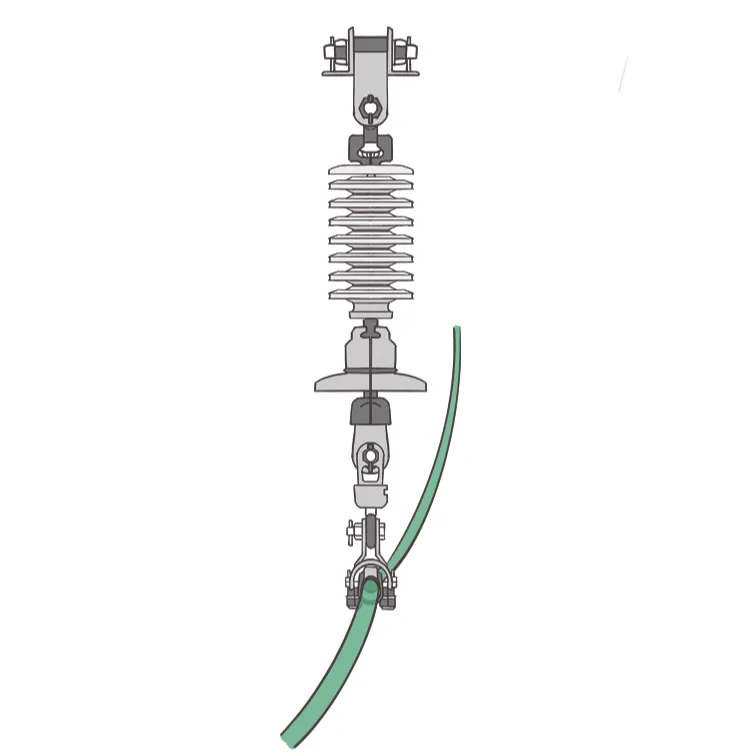
The voltage class is generally 110 kV, 35 kV and below. Some 220 kV lines also use single-split conductors.
Two-split conductors:
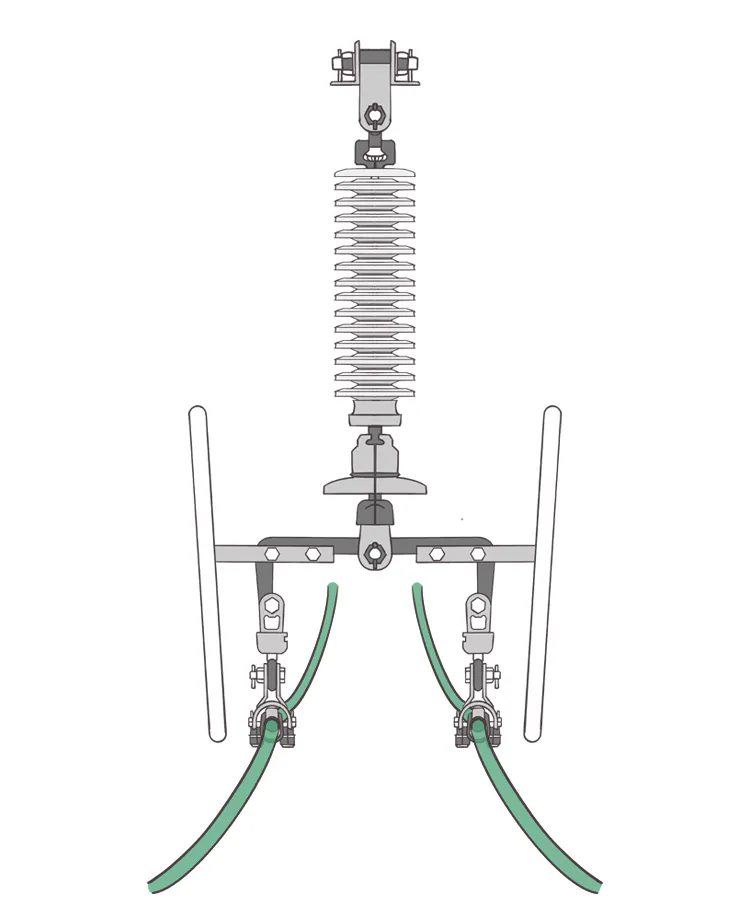
The voltage class is 220 kV or 330 kV, and 330 kV transmission lines are currently only constructed in the northwest region, so in Sichuan, the voltage level of the two split wires is 220 kV.
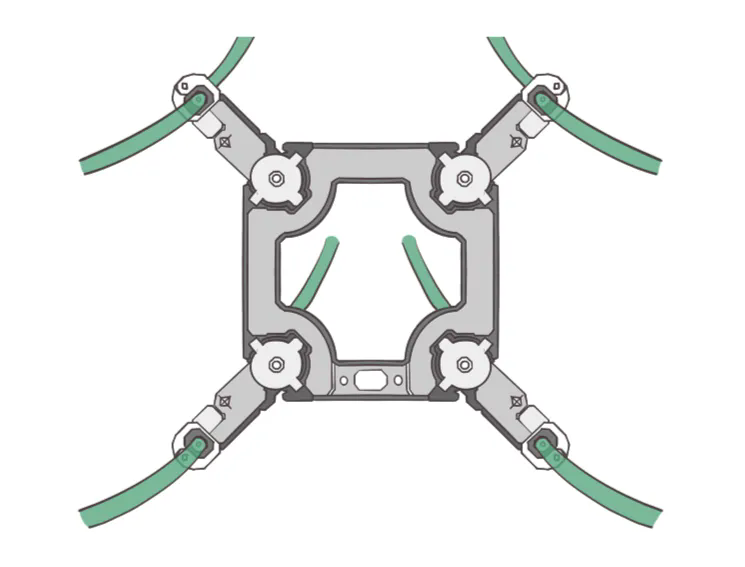
Four-split conductors: The voltage class is 500 kV
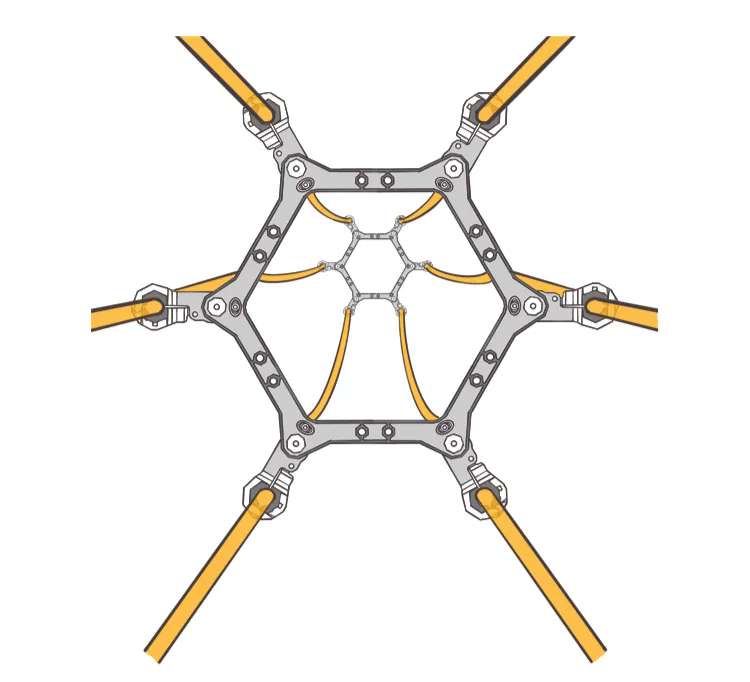
Six-split conductors: The voltage level is generally 750 kV. Currently, only the northwest region has built transmission lines with 750 kV voltage level.
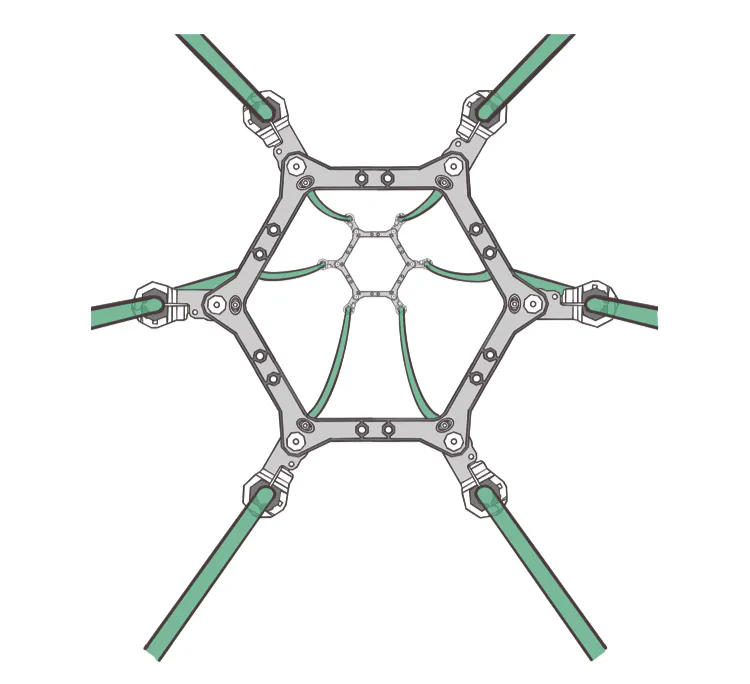
The splitting situation of DC transmission lines is as follows:
Four-split conductors: The voltage class is ±500 kV
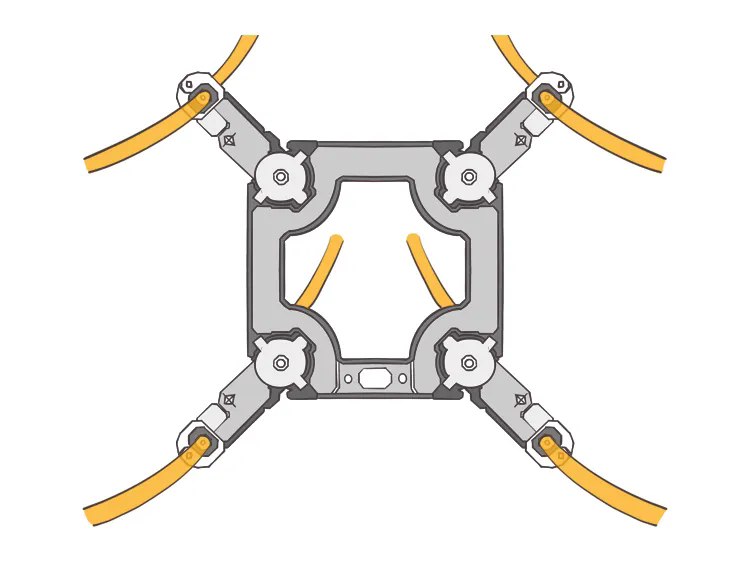
Six-split conductors: The voltage class is ±800 kV